Software testing and quality assurance have become critical components of successful software development in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. As businesses increasingly rely on digital solutions, ensuring that applications function flawlessly, securely, and efficiently has never been more critical. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals, benefits, and advanced approaches to modern software testing and quality assurance practices.
Understanding Software Testing and Quality Assurance: The Foundation of Reliable Software
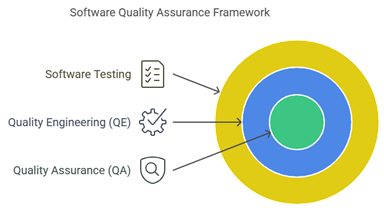
Software testing and quality assurance represent systematic processes designed to evaluate software applications for functionality, performance, security, and usability. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct yet complementary purposes in the software development lifecycle.
Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on the processes and procedures that prevent defects during software development. It’s a proactive approach that establishes a framework for building quality into the product from the beginning rather than testing it later. QA activities include establishing standards, conducting reviews, and implementing best practices throughout development.
Quality Engineering (QE) expands beyond traditional QA by encompassing the entire software development lifecycle. QE integrates quality practices early in the process, including automation, performance testing, and security measures, ensuring comprehensive quality control from inception to deployment.
The Critical Role of Software Testing and Quality Assurance in Business Success
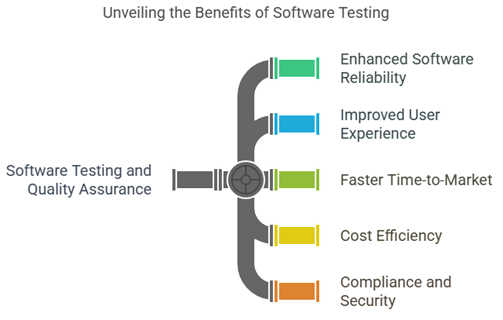
Implementing robust software testing and quality assurance processes offers numerous benefits for businesses across all industries:
- Enhanced Software Reliability: Thorough testing ensures applications perform consistently even under challenging conditions, building user trust.
- Improved User Experience: Businesses deliver smoother, more intuitive user experiences by identifying and resolving issues before release.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Unlike common misconceptions, effective QA accelerates development cycles by catching issues early when they’re less expensive and time-consuming.
- Cost Efficiency: Finding and fixing defects during development is significantly less costly than addressing them after deployment, with some industry estimates suggesting that post-release fixes can cost 4-5 times more.
- Compliance and Security: Proper testing ensures applications meet industry standards and regulatory requirements, protecting the business and its customers.
The Systematic Process Approach to Software Testing and Quality Assurance
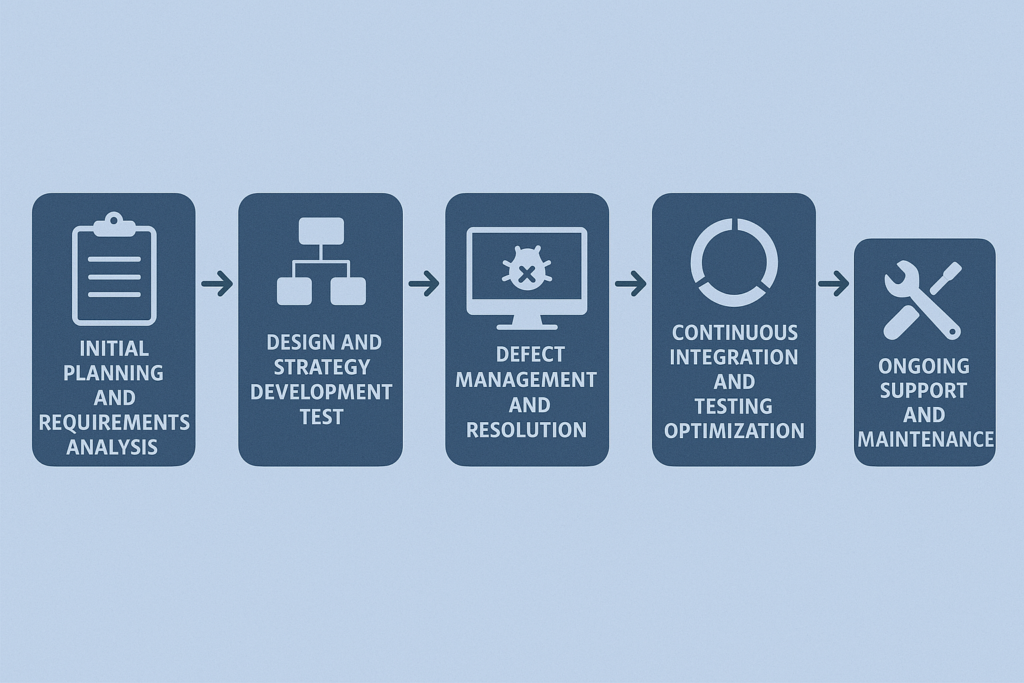
A methodical approach to software testing and quality assurance ensures comprehensive coverage and optimal results:
1. Initial Planning and Requirements Analysis
The foundation begins with thorough stakeholder collaboration to clearly define testing objectives, scope, and success metrics. This phase includes:
- Collaborative stakeholder engagement to understand project goals
- Defining clear testing objectives based on business requirements
- Developing comprehensive testing strategies
- Identifying key performance indicators
- Assessing and planning for potential risk factors
2. Design and Strategy Development Test
Creating a blueprint for testing activities ensures nothing is overlooked:
- Developing test cases and scenarios based on requirements
- Creating test scripts and automation plans
- Designing test environments that simulate real-world conditions
- Defining test data requirements and preparing necessary datasets
- Aligning test designs with business objectives
3. Test Execution and Monitoring
The active testing phase involves:
- Executing manual and automated test cases according to the plan
- Monitoring progress and tracking issues
- Performing various types of testing (regression, functional, performance)
- Documenting test results and findings
- Analyzing results to identify patterns and improvement areas
4. Defect Management and Resolution
When issues are discovered, a structured approach ensures proper handling:
- Logging and categorizing defects based on severity
- Collaborating with development teams on prioritization
- Retesting resolved issues
- Documenting resolution processes
- Conducting root cause analysis to prevent recurrence
5. Continuous Integration and Testing Optimization
Modern testing approaches incorporate:
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines
- Optimization of test automation frameworks
- Implementation of feedback loops
- Regular review and updates to testing practices
- Adaptation to new testing technologies
6. Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Quality assurance doesn’t end at deployment:
- Providing continued support for testing environments
- Conducting periodic reviews of testing strategies
- Offering training for QA teams
- Ensuring long-term effectiveness of testing processes
- Monitoring industry trends to continuously improve practices
Advanced Approaches in Modern Software Testing and Quality Assurance
As technology evolves, so do the approaches to software testing and quality assurance:
Low Code and No Code Testing
As businesses increasingly adopt low code and no code development platforms to accelerate application delivery, specialized testing approaches have emerged:
- Streamlined Testing Processes: Efficient testing methodologies specially designed for low code and no code applications
- Enhanced Application Performance: Early identification of issues to ensure optimal performance
- Accelerated Development Cycles: Quicker release processes through efficient testing
- Cost Savings: Reduced testing costs through streamlined approaches
- Increased Reliability: Ensuring flawless operation across all scenarios
Test Automation Frameworks
Automation has revolutionized software testing by enabling faster, more reliable test execution:
- Consistent Testing: Uniform test execution across different environments
- Increased Efficiency: Faster testing through reusable scripts
- Reduced Manual Effort: Minimizing repetitive manual tasks
- Scalability: Easy adaptation to accommodate changes
- Improved Accuracy: Reduction in human error for more precise outcomes
Low Code and No Code Automation Frameworks
These specialized frameworks bring automation benefits to applications built on low code and no code platforms:
- Simplified Automation: Easier automation with minimal setup
- Efficient Testing: Faster, more reliable results
- Seamless Integration: Effortless integration with existing platforms
- Reduced Time-to-Market: Accelerated development cycles
- Cost Optimization: Reduced manual testing expenses
Industry Applications for Software Testing and Quality Assurance
Software testing and quality assurance practices deliver value across various industries:
Banking and Financial Services
In the financial sector, testing ensures the security and functionality of systems that handle sensitive transactions and customer data. Rigorous testing validates data integrity, transaction accuracy, and regulatory compliance, building customer trust and preventing costly errors.
Healthcare
For healthcare applications, testing verifies the reliability and accuracy of medical software and patient management systems. This ensures patient data security, system interoperability, and compliance with healthcare regulations, ultimately contributing to better patient care.
Retail and E-commerce
In retail environments, testing optimizes the performance and usability of shopping platforms. This enhances customer experience by ensuring smooth checkout processes, accurate inventory management, and secure payment processing.
Media and Entertainment
Testing in media applications ensures content delivery platforms perform seamlessly. This includes validating streaming quality, content protection measures, and cross-device compatibility for uninterrupted viewing experiences.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, testing verifies the safety and functionality of in-car systems, including infotainment, navigation, and driver assistance technologies. This ensures reliable performance and user safety in critical driving scenarios.
Selecting the Right Tech Stack for Software Testing and Quality Assurance
A comprehensive software testing and quality assurance approach requires the right combination of tools and technologies:
Performance Testing Tools
These tools evaluate how systems perform under various load conditions, identifying bottlenecks before they impact users.
Security Testing Solutions
Security testing tools identify vulnerabilities and ensure applications protect sensitive data from potential threats.
Automation Testing Frameworks
These frameworks enable efficient execution of repetitive tests, improving coverage and reducing manual effort.
CI/CD Integration
Integration with continuous integration and delivery pipelines ensures testing is performed automatically with each code change.
Test Management Systems
These systems organize test cases, track execution, and provide reporting on test coverage and results.
API Testing Tools
API testing ensures that the interfaces between different software components function correctly.
Cloud-Based Testing Solutions
Cloud platforms enable testing across different environments and configurations without extensive infrastructure investments.
Best Practices for Implementing Effective Software Testing and Quality Assurance
To maximize the benefits of software testing and quality assurance:
- Shift Left in Testing: Integrate testing early in the development process rather than treating it as a final step.
- Prioritize Test Automation: Identify repetitive tests that can be automated to increase efficiency and coverage.
- Establish Clear Quality Metrics: Define what success looks like through measurable quality indicators.
- Implement Continuous Testing: Make testing an ongoing process within development cycles rather than a one-time event.
- Balance Manual and Automated Testing: Recognize that some tests require human intuition while others benefit from automation.
- Maintain Test Data Quality: Ensure test data accurately represents real-world scenarios.
- Perform Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing: Verify that applications work consistently across different platforms.
- Conduct Regular Security Testing: Make security a continuous focus rather than a one-time verification.
Conclusion: The Future of Software Testing and Quality Assurance
As technology continues to evolve, software testing and quality assurance practices will adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are already transforming testing by predicting potential issues, generating test cases, and automating analysis of test results.
The rise of DevOps and continuous delivery models has further elevated the importance of integrated, automated testing approaches. Organizations that embrace comprehensive software testing and quality assurance methodologies position themselves for faster innovation, higher customer satisfaction, and stronger competitive advantage.
By investing in robust software testing and quality assurance processes, businesses ensure their applications not only meet user expectations but exceed them, delivering exceptional digital experiences that drive business success.