In today’s fast-paced tech landscape, product development demands speed, precision, and collaboration. Enter autonomous agents for product development—AI-powered tools that handle complex tasks independently, streamlining workflows and boosting efficiency. These intelligent agents act as virtual team members, automating everything from ideation to deployment. If you’re a product manager, engineer, or business leader looking to accelerate your processes, understanding how autonomous agents integrate into the product lifecycle can be a game-changer.
This guide explores the role of autonomous agents for product development, highlighting key agents like the PO-Agent, BI-Agent, Head Engineer Agent, Developer Agent, QA Agent, and Infra Agent. We’ll dive into their benefits, real-world applications, and tips for implementation, all while drawing on agile methodologies and cutting-edge AI trends.
What Are Autonomous Agents in Product Development?

Autonomous agents for product development are AI systems designed to perform tasks with minimal human oversight. Unlike traditional software tools, these agents learn from data, make decisions, and adapt in real-time. They fit seamlessly into the product development lifecycle, covering stages like planning, design, coding, testing, and infrastructure management.
Imagine a virtual team where each member specializes in a core function:
- PO-Agent: Focuses on product vision and backlog prioritization.
- BI-Agent: Analyzes data for informed decision-making.
- Head Engineer Agent: Oversees technical architecture and team coordination.
- Developer Agent: Handles coding and feature implementation.
- QA Agent: Ensures quality through rigorous testing.
- Infra Agent: Manages deployment and infrastructure scalability.
The Benefits of Using Autonomous Agents for Product Development
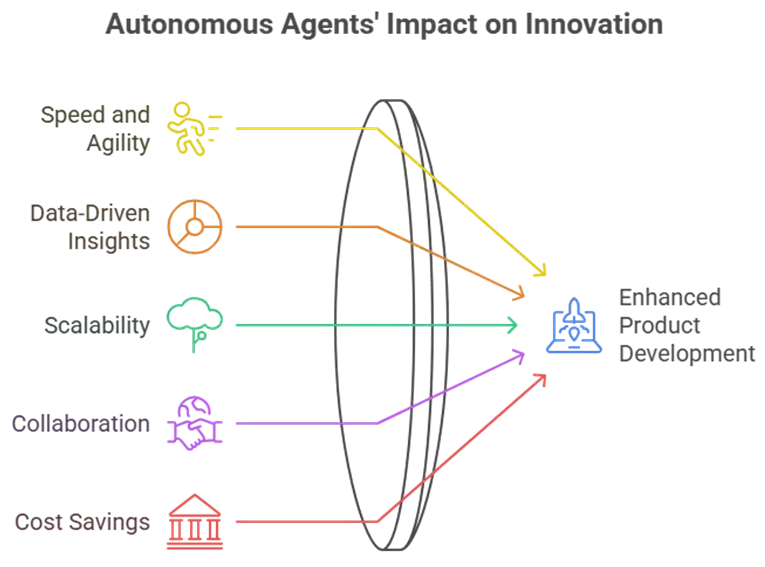
Adopting autonomous agents for product development isn’t just about efficiency, it’s about transforming how teams innovate. Here are the key advantages:
- Enhanced Speed and Agility: Agents like the Developer Agent can generate code snippets in seconds, while the PO-Agent prioritizes tasks based on real-time market data. This supports agile development with AI, allowing teams to iterate faster.
- Data-Driven Insights: The BI-Agent pulls from vast datasets to provide actionable recommendations, helping you spot trends before they impact your product roadmap.
- Scalability Without Overhead: The Infra Agent automates cloud deployments, ensuring your infrastructure scales effortlessly as your product grows.
- Improved Collaboration: The Head Engineer Agent facilitates code reviews and mentoring, bridging gaps between human teams and AI tools.
- Cost Savings: By automating repetitive tasks, these agents reduce the need for large teams, potentially saving up to 30% on development costs (based on McKinsey’s AI productivity studies; source: McKinsey AI Report).
In essence, autonomous agents for product development empower small teams to compete with enterprise giants, fostering innovation in industries like SaaS, e-commerce, and fintech.
Key Autonomous Agents and Their Roles in the Product Lifecycle
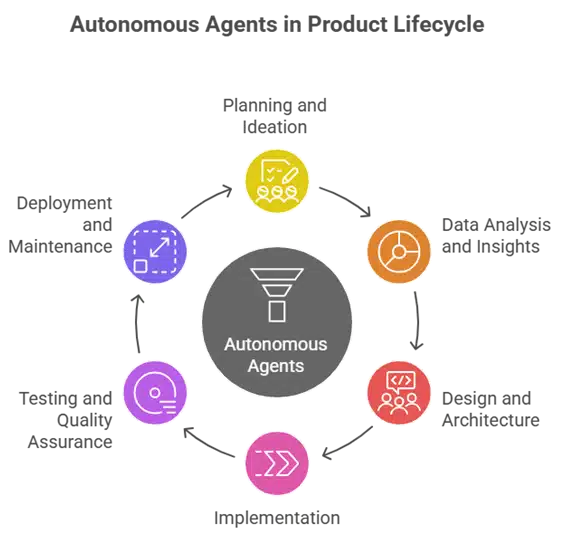
Let’s break down how specific autonomous agents for product development contribute to each phase of the product lifecycle. These agents are designed to work in tandem, creating a cohesive ecosystem.
1. Planning and Ideation with the PO-Agent
The PO-Agent acts as your virtual product owner, defining vision and gathering requirements. It uses natural language processing to analyze stakeholder feedback and prioritize backlogs in tools like Jira. For instance, if you’re developing a new app feature, the PO-Agent can scan user reviews and suggest priorities, ensuring alignment with business goals.
2. Data Analysis and Insights with the BI Agent
In the research phase, the BI-Agent excels at turning raw data into insights. It integrates with tools like Tableau for visualizations and tracks KPIs to forecast market needs. This agent is invaluable for autonomous agents for product development in data-heavy projects, such as predicting user churn in a subscription service.
3. Design and Architecture with the Head Engineer Agent
The Head Engineer Agent oversees technical strategy, designing scalable architectures and conducting virtual code reviews. It mentors junior developers by suggesting best practices and integrates with cloud services for seamless collaboration. This makes it a cornerstone for teams adopting AI-driven agents in product engineering.
4. Implementation with the Developer Agent
At the core of building, the Developer Agent writes, debugs, and deploys code in languages like Python or JavaScript. Using version control like Git, it automates feature development, allowing human developers to focus on creative problem-solving. Real-world example: In a mobile app project, it could generate backend APIs autonomously.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance with the QA Agent
Quality is non-negotiable, and the QA Agent handles it through automated testing scripts It identifies bugs, runs regression tests, and ensures compliance with standards. For autonomous agents for product development, this means fewer post-launch issues and higher user satisfaction.
6. Deployment and Maintenance with the Infra Agent
Finally, the Infra Agent manages servers, CI/CD pipelines, and monitoring on platforms like AWS or Azure. It automates security configs and scales resources dynamically, making it essential for ongoing product maintenance.
By integrating these agents, your product development process becomes a well-oiled machine. For more on agent collaboration, check out our guide on AI Agent Workflows.
How to Implement Autonomous Agents in Your Product Development Workflow
Ready to get started? Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Assess Your Needs: Identify pain points, such as slow testing or inefficient planning.
- Choose the Right Agents: Start with essentials like the PO-Agent for planning and Developer Agent for coding.
- Integrate Tools: Connect agents to your existing stack (e.g., GitHub, Slack) for seamless operation.
- Train and Monitor: Use human oversight initially to fine-tune AI behaviors.
- Measure Success: Track metrics like deployment frequency and bug rates.
Remember, successful implementation of autonomous agents for product development requires ethical AI practices—ensure data privacy and bias checks.
Challenges and Future Trends in Autonomous Agents for Product Development
While powerful, autonomous agents for product development aren’t without hurdles. Integration complexity and AI hallucinations can arise, but advancements in machine learning are addressing these. Looking ahead to 2025, expect more hybrid human-AI teams and agents powered by generative AI for even smarter automation.
In summary, autonomous agents for product development are reshaping the industry, making processes faster, smarter, and more collaborative. By incorporating agents like the PO-Agent, BI-Agent, and others, your team can focus on what matters: innovation.
If you have questions or want to explore these agents further, contact us or dive into our resources on AI automation.