Software quality can make or break a business. As development cycles accelerate and user expectations soar, traditional quality assurance methods struggle to keep pace. Manual testing bottlenecks delay releases, human error lets defects slip through, and QA teams spend 60-70% of their time on repetitive tasks rather than strategic quality improvements.
Enter the QA Agent—an autonomous Quality Intelligence engine that transforms how organizations validate software. Unlike conventional automated testing tools that simply replay scripted actions, QA Agents leverage artificial intelligence to think, adapt, and evolve throughout the entire testing lifecycle.
What is a QA Agent?
A QA Agent is an AI-powered autonomous system that manages the complete software testing workflow from requirements analysis to deployment validation. Think of it as a virtual Quality Assurance architect that never sleeps, never misses edge cases, and continuously learns from every test cycle.
The ideyaLabs QA Agent within AiLabs exemplifies this paradigm shift. It doesn’t just execute tests, understands requirements, generates comprehensive test strategies, creates intelligent test data, executes validation at machine speed, and manages defect resolution cycles autonomously.
How QA Agents Work: The Intelligent Testing Lifecycle
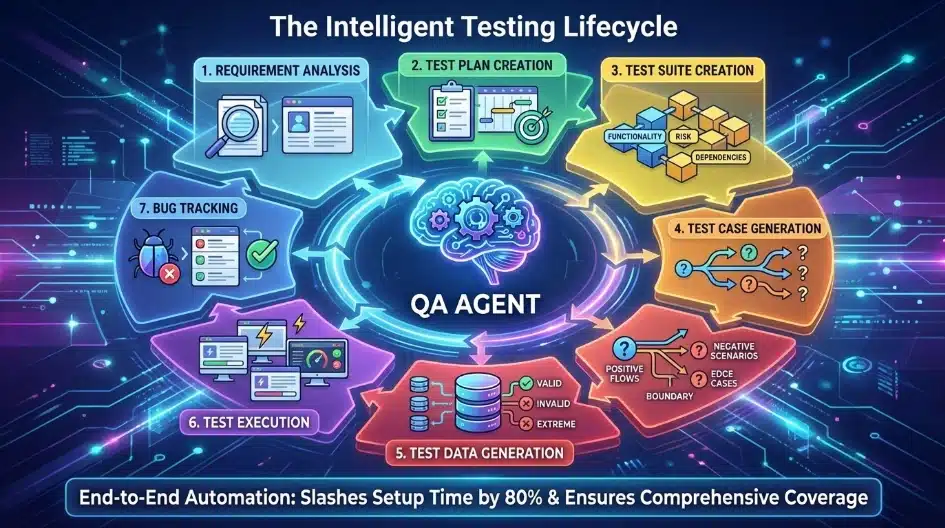
QA Agents operate through a structured seven-phase workflow that mirrors—and enhances—human QA expertise:
- Requirement Analysis: The agent parses project specifications, user stories, and acceptance criteria to understand what needs validation
- Test Plan Creation: It designs comprehensive testing strategies including objectives, methodologies, test types, and realistic timelines
- Test Suite Creation: The agent organizes test cases into logical suites based on functionality, risk profiles, and dependencies
- Test Case Generation: It automatically creates detailed test scenarios covering positive flows, negative scenarios, boundary conditions, and edge cases
- Test Data Generation: The agent synthesizes realistic datasets including valid inputs, invalid entries, and extreme edge conditions
- Test Execution: It runs tests on a scale, monitors results in real-time, and generates actionable reports with pass/fail summaries
- Bug Tracking: The agent automatically logs defects with complete context, tracks resolution status, and verifies fixes
This end-to-end automation slashes setup time by 80% while ensuring comprehensive coverage that human testers might miss under deadline pressure.
Why QA Agents Outperform Traditional Testing

Traditional automated testing relies on pre-written scripts that break when interfaces change. QA Agents bring cognitive intelligence to the process:
Adaptive learning: They adjust testing strategies based on application changes rather than requiring manual script updates. When a button moves or a field name changes, the agent recognizes the functional equivalence and adapts automatically.
Context awareness: Instead of blindly checking that code executes, QA Agents validate that software delivers actual business value. They understand user journeys and test from the perspective of real-world scenarios.
Comprehensive coverage: Where human testers might focus on happy paths under time constraints, QA Agents systematically validate every scenario—from standard workflows to chaos engineering stress tests that simulate system failures.
Closed-loop resolution: When defects surface, the agent doesn’t just log them. It provides detailed reproduction steps, expected versus actual behavior, relevant logs, and automatically verifies fixes once developers submit patches.
Types of Testing QA Agents Handle
Modern QA Agents support the full spectrum of testing methodologies:
- Unit testing validates individual components in isolation
- Integration testing ensures modules work together correctly
- Functional testing confirms features match requirements precisely
- Regression testing automatically detects when new code breaks existing functionality
- Performance testing measures response times under various load conditions
- Security testing probes for vulnerabilities and compliance gaps
The ideyaLabs QA Agent handles all these testing types within a unified framework, eliminating the need for separate tools and reducing integration complexity.
Real-World Impact: From Weeks to Minutes
Consider a typical enterprise software release cycle. Traditional QA might require:
- 2-3 days for test planning and case writing
- 5-7 days for test execution across multiple scenarios
- 1-2 days for bug documentation and developer handoffs
- Another cycle of retesting after fixes
That’s 2-3 weeks minimum, often longer for complex applications.
With a QA Agent, this compresses dramatically:
- Requirements parsed and test plans generated in under an hour
- Comprehensive test suites executed in parallel within hours
- Bugs automatically logged with full context for immediate developer action
- Fix verification automated within the same day
The result? Feedback loops measured in hours instead of weeks, enabling true continuous deployment.
QA Agents and CI/CD Integration
QA Agents shine brightest when integrated into continuous integration and continuous deployment pipelines. They trigger automatically on every code commit, providing instant quality feedback before changes reach production.
Parallel execution runs hundreds of test cases simultaneously across distributed infrastructure, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing waiting times.
Instant feedback delivers test results to developers within minutes, enabling them to fix issues while the code context is still fresh in their minds.
Automated gates prevent defective code from advancing through the pipeline, maintaining quality standards without manual checkpoints.
The Human-in-the-Loop Model
Despite their autonomy, QA Agents work best alongside human expertise. While they handle the repetitive grunt work of test creation and execution, human QA professionals provide strategic oversight:
- Reviewing generated test plans for business logic alignment
- Defining risk-based testing priorities
- Making final release decisions for critical deployments
- Investigating anomalies that require domain expertise
This division of labor lets QA teams focus on high-value activities like exploratory testing, usability evaluation, and quality strategy while agents handle the mechanical validation work.
Choosing the Right QA Agent Solution
When evaluating QA Agent platforms, consider these factors:
Integration capabilities: Does it connect seamlessly with your existing development tools, bug trackers, and CI/CD systems?
Test data intelligence: Can it generate realistic synthetic data that protects privacy while enabling thorough testing?
Maintenance burden: Does it require constant script updates, or does it self-heal when applications change?
Scalability: Will it handle your testing volume as your application and team grow?
The ideyaLabs QA Agent within AiLabs addresses all these requirements through enterprise-grade architecture designed for complex, rapidly evolving software ecosystems.
The Future of Quality Assurance
QA Agents represent more than automation—they’re a fundamental shift in how organizations think about software quality. Rather than treating QA as a pre-release checkpoint, they enable continuous quality intelligence throughout the development lifecycle.
As AI capabilities advance, QA Agents will become even more sophisticated. Future iterations will predict where defects are likely to emerge based on code complexity metrics, automatically generate test scenarios from production monitoring data, and even suggest architectural improvements to enhance testability.
For organizations serious about software quality, deployment velocity, and engineering efficiency, QA Agents aren’t a luxury—they’re becoming essential infrastructure.